Structure and Function of Animal Cell
The cell serves as the fundamental structural and functional unit of living organisms. Comprising various components, each with specific functions, cells play a vital role in the existence of living entities. Organelles, small sub-cellular bodies found in the cytoplasm, contribute to the specialized functions within the cell.
Types of Eukaryotic Cells
All living organisms are composed of cells, and the cell is recognized as the smallest unit of life. There are two primary types of eukaryotic cells: Animal cells and Plant cells. Eukaryotic cells possess a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Notably, animal cells lack a cell wall and chloroplasts.
Animal Cell Membrane
Composition and Structure
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, envelops the animal cell. Chemically, it is composed of proteins, lipids, and a small quantity of carbohydrates. The fluid mosaic model represents the structure of the membrane, suggesting a fluid phospholipid bilayer with embedded protein molecules.
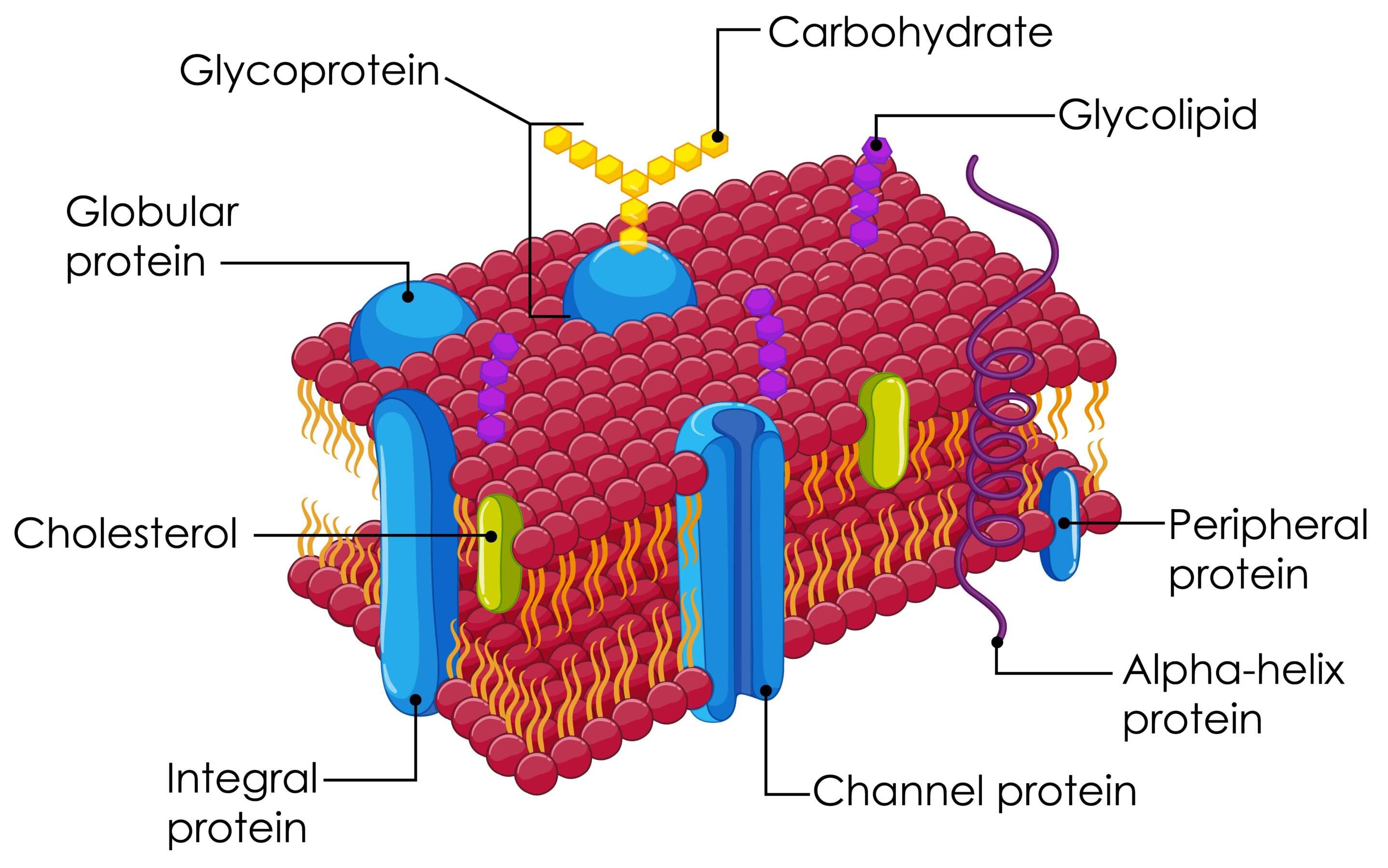
Functions
The cell membrane serves as the point of contact between the cell and its environment. It acts as a barrier, preventing the escape of cell contents, and regulates the entry and exit of substances. Referred to as a differentially or selectively permeable membrane, it allows the passage of oxygen, food, and water while excluding harmful substances.
Nucleus
Location and Components
Situated in the central region of the cell, the nucleus is a crucial organelle. It comprises a double nuclear membrane, nucleoplasm, nucleolus, and chromosomes. The nuclear envelope, a double membrane with numerous pores, surrounds the nucleus.
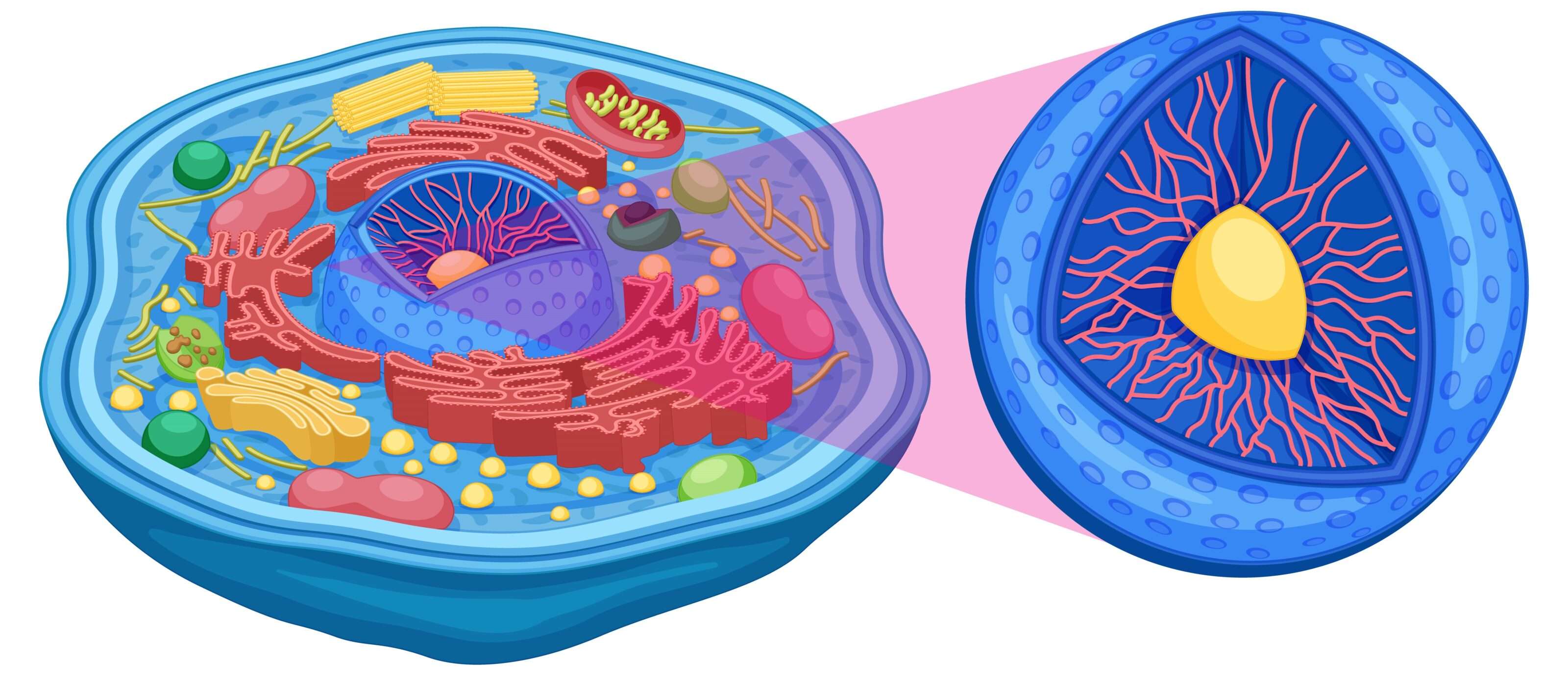
Nuclear Components
The nucleoplasm is the fluid inside the nucleus, the nucleolus is a dark staining region, and chromosomes are thread-like structures. Chemically, chromosomes consist of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and protein. The centromere, a constriction in the chromosome, is a key structural element.
Control of Cell Activities
The nucleus assumes a pivotal role in controlling all cellular activities. It governs essential processes, ensuring the coordination and regulation of functions within the cell.
Learn Next : Structure and Function of Animal Cell (Part-II)
Go Check out and Learn: MCQs on Classification and Taxonomy




This is gold!