What is Obstetrics?
The branch of medical science is concerned with the care of women’s reproductive tracks during pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. It is often abbreviated by OB or Obs.
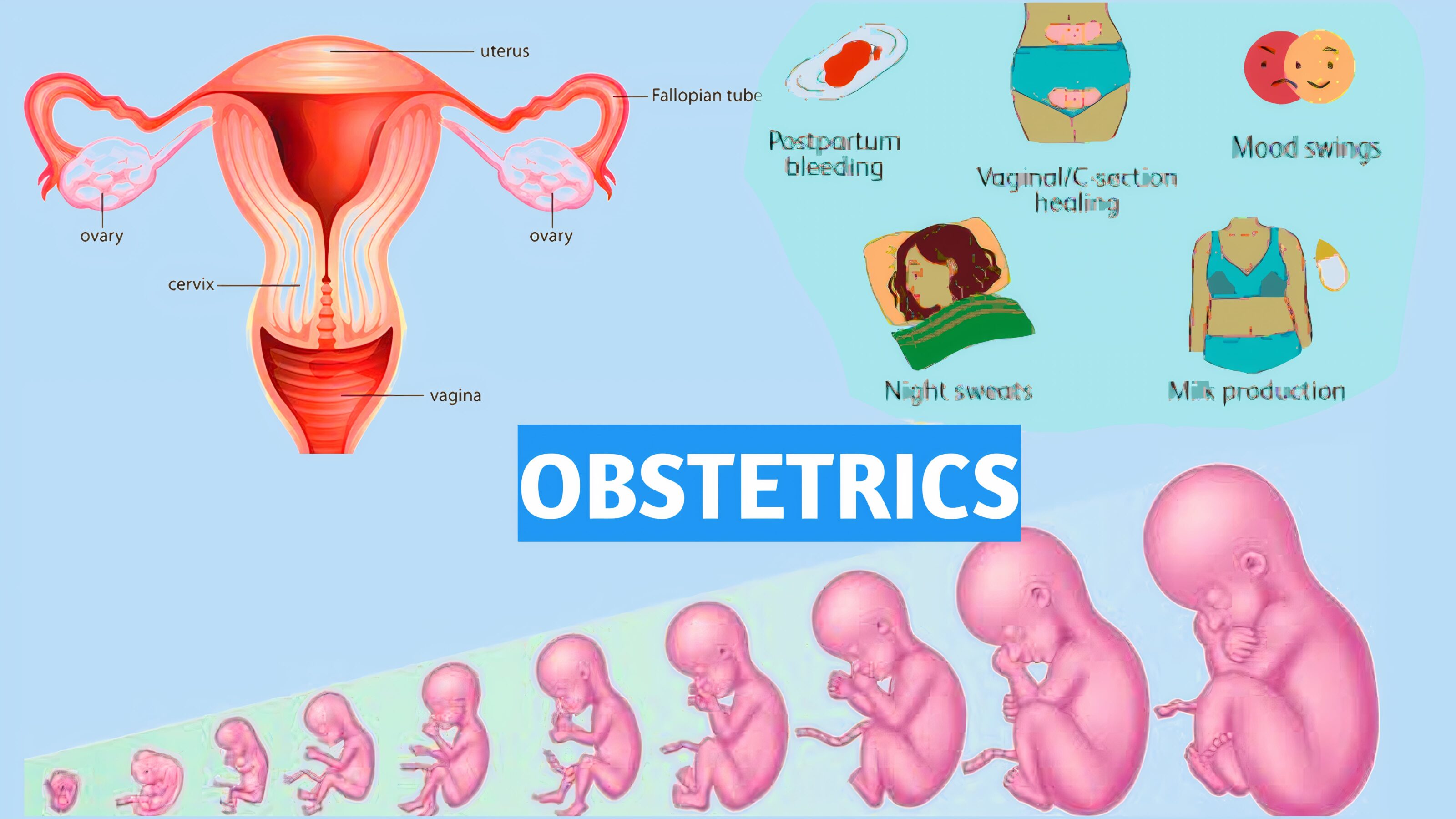
The main point related to Obstetrics:
- Antenatal care
- Examination of women during pregnancy.
- Supervision should be on a regular basis for a pregnant lady from developing embryo till pregnancy.
Aims and Objectives of Obstetrics:
- To screen high-risk patients e.g. pregnancy-induced hypertension.
- To treat complications e.g., oligohydramnios, heavy bleeding.
- To educate the mother about antenatal care and labor.
- To remove the fear of pregnant ladies related to the mode of pregnancy by counseling.
- To gain confidence before labor.
- To ensure normal delivery.
- To deliver a healthy lady.
- To motivate couples for family planning.
History taking to Diagnosis of the pregnant lady:
- Biometric data (like name, age)
- Year of marriage,
- Presenting complaint,
- History of presenting complaint,
- Past medical and surgical history,
- Drug history,
- Personal history,
- Family history,
- Ask the date of the last menstrual period(LMP),
- Now find the Expected Date of Delivery(EDD),
How to find EDD;
If a lady tells you LMP 01-02-2021 then use Naegele's Formula to find EDD;
For Example:
- Addition of 7 on the day like 1+7=8
- Addition of 9 on the month like 2+9=11 (addition of month should be by keeping the name of months in mind like in the mentioned above situation: Feb, Mar, Apr, May, Jun, Jul, Aug, Sept, Oct, Nov) By this way you can easily find the EDD of if it forward to next year.
- So the EDD of above mention LMP is 08-11-2021.
History Of Trimesters:
Pregnant females often come to a doctor with the following complaints:
During 1st Trimester:
- Ectopic pregnancy,
- Constipation (Due to fetal size),
- Back pain,
- Amenorrhea,
- Bleeding (Clotted or continuous)
- Hyperemesis gravidarum (severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy)
- Heartburn,
- Insomnia,
- Increase urine,
- Increase urinary tract infection,
2nd Trimester:
- Anemia,
- Miscarriage,
- Bleeding,
- Passage of vesicles like grapes (Molar Pregnancy),
- Lower abdomen pain,
3rd Trimester:
- Pain/Bleeding,
- Placenta fundus,
- Oligomenorrhea,
- Ovarian cyst,
- Polymenorrhagia,
- Fibroid,
- Increase lipids,
- Increase blood pressure,
- Gallstones,
- Peptic ulcers worsen,
- Cystitis,
- Colic pain,
- Gynae problem,
Table for Obstetrics History:
| No. of pregnancy | Duration | Mode of Delivery | Place of delivery | Complications of pregnancy | Baby conditions | Vaccination/ Breastfeeding | Gender of Baby |
| 1 | 35 weeks term | C-section | Hospital | Hemorrhage Infection | Death | non | Male |
| 2 | 9 months | SVD (Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery) | Home | None | Alive | Done | Female |
Complications:
- Post-partum hemorrhage,
- Congenital infection
- Psychological symptoms,
How to take a history of a pregnant female?
Normal Pregnancy:
The following points should keep in mind before taking a history of a pregnant female,
- Normal duration 37 weeks or 9 months (this is called Term)
- Preterm-> Delivery of baby before 37 weeks,
- Post-term-> Delivery of baby after 40 weeks.
Gynae History:
- Methods of contraception,
- Cervical Pap Smear test,
- Coital problems,
- Menstrual history,
Conception History:
- Spontaneous,
- Long-term infection,
- History of (IVF) In Vitro Fertilization (Assisted Reproductive Method),
Past medical and surgical history:
- Heart disease (like HTN)
- DM (Diabetes Mellitus)
- Epilepsy
- Thyroid disorder
- Autoimmune disease
- Asthma,
- Psychological disorders,
- Kidney disease,
- Hepatitis,
- Any surgical history,
- Drug history,
- Folic Acid history,(If a woman doesn’t get enough folic acid during pregnancy, the baby is at high risk for neural tube defects)
- Allergic history (Drugs or others)
Family History:
- Congenital anomaly,
- Cousin marriage,
- Family disease,
Personal History:
- Smoking/alcohol,
- Contraception history,
- Education or job history,
- Social History:
- Partner age/job/health/relationship(stable domestic violence)
Relaxed / Flexed Patient,
- Vitals are important for Obs. Pt
- If 2nd trimester ends and 3rd trimester starts then abdominal physical examinations is required;
- Inspection,
- Palpation,
- Percussion,
- Auscultation,
- Baby position (Long /Cephalic)
- The shape of the uterus (Breach / Breach transverse).
Systemic inquiry:
Neurological status,
- Nutritional status,
- Psychosis,
- Facial features,
- Skin pigmentation (Cheek, Neck)
- Legs / Feet / Gait of the patient (any limbs problems)
- Breast examination
- Blood pressure
Gestational Hypertension (Preeclampsia means elevated blood pressure after 20 weeks of gestation which is about ≥ 140 mmHg systolic or ≥ 90 mmHg diastolic)
- Heart rate (during pregnancy a bit increase heart rate is normal)
- Birth State
- Respiratory rate (During pregnancy a bit increased respiratory rate is also normal this is because of the pressure on the diaphragm)
- Temperature,
- Nails (iron-deficient anemia)
- Tongue examination
- Weight + Height (BMI)
- BMI = 22-25 normal, 25-28 overweight, 28-35 obese
- Fetal heart rate,
- Fetal movements (usually start at 20 weeks)
- On palpitation, we can feel the head,
- Fundal height (also called McDonald’s rule, is a measure of the size of the uterus which is used to check the fetal growth and development during the gestational period. And this is measured from the top of the mother’s uterus to the top of the mother’s pubic symphysis. At 20 weeks of gestation, the healthcare provider measures the fundal height. Fundal height usually equals the number of weeks the pregnant female has. For example, give and take 2 cm either way, for a 30-week pregnant female the fundal height should be somewhere between 28 cm and 32cm). Fundal height larger than expected may show the pregnant lady may have too much amniotic fluid or more than one baby or the baby is larger than expected.
Prenatal Care:
Prenatal care is also called antenatal care. It is the period in which the individual grows from fertilization until birth. It is a type of preventive health care and the main goal of prenatal care is to provide regular checkups that allow doctors or midwives to treat and prevent potential health care problems throughout the course of pregnancy and to promote a healthy lifestyle that benefits both mothers and babies.
Complete details of prenatal care will be published in a new post soon.


very nice information thanks for sharing
Itís difficult to find educated people about this topic, but you seem like you know what youíre talking about! Thanks
Im very happy to uncover this great site. I need to to thank you for ones time for this fantastic read!! I definitely enjoyed every bit of it and I have you book marked to see new things in your blog.
Im very happy to find this web site. I wanted to thank you for your time just for this fantastic read!! I definitely liked every bit of it and i also have you book-marked to see new things in your website.