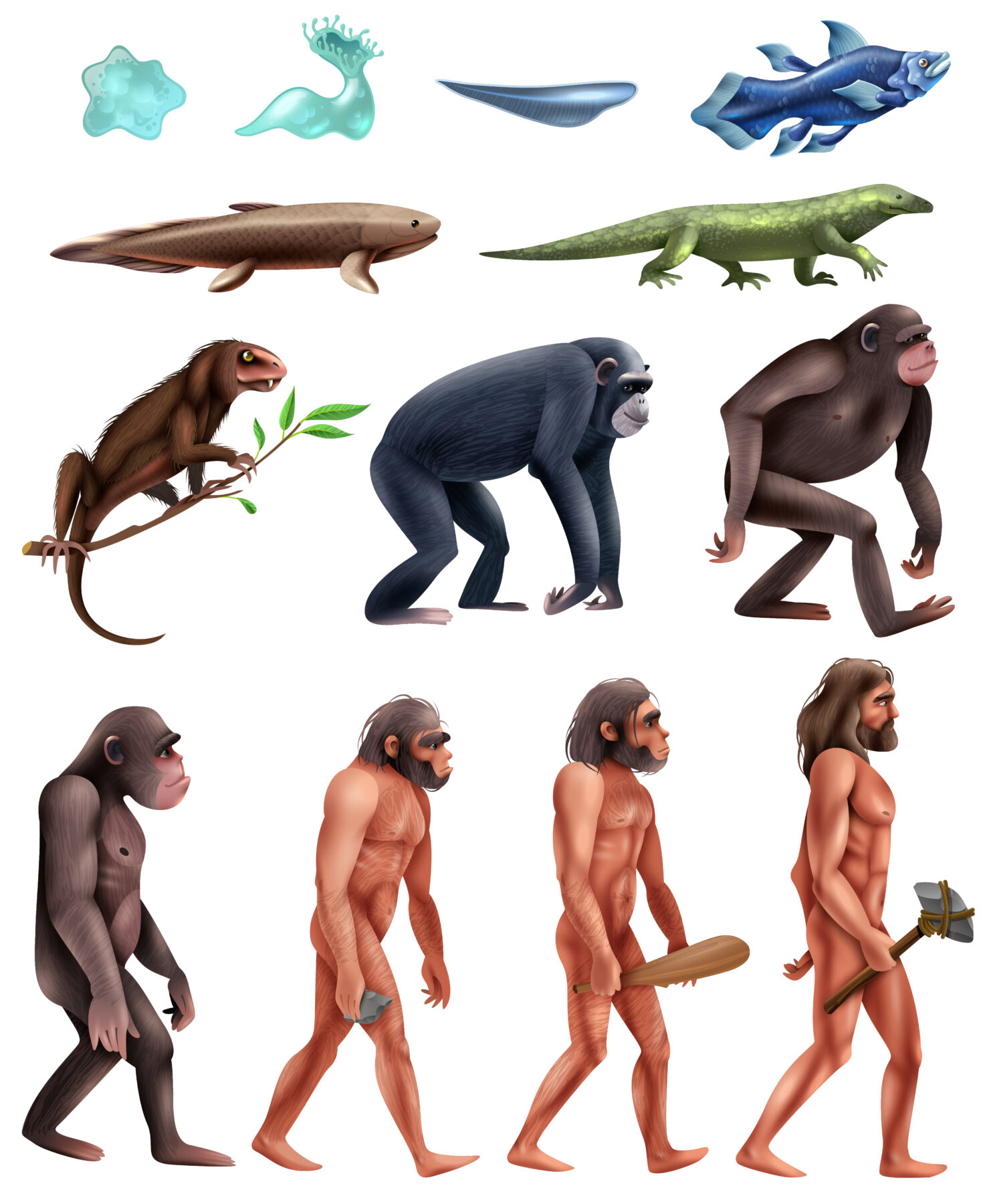
Evolution in biology is the fundamental concept that explains how living organisms change over generations through variations in inherited traits. It provides a scientific framework to understand the origin of species, biodiversity, and the adaptation of organisms to their environment. Evolution is not a sudden process; rather, it is a slow and continuous change occurring over millions of years, shaping life on Earth.
The theory of evolution forms the backbone of modern biological sciences, influencing genetics, ecology, medicine, and biotechnology.
Quiz
Available options: 1 to 20
Historical Background of Evolution
The idea of evolution existed long before modern science, but it was Charles Darwin who provided a scientific explanation through his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Darwin proposed that organisms evolve through natural selection, where individuals with favorable traits survive and reproduce more successfully.
Later discoveries in genetics strengthened the theory, giving rise to the Modern Synthetic Theory of Evolution, which combines Darwin’s ideas with Mendelian genetics.
Mechanisms of Evolution in Biology
Several mechanisms drive evolution in biology, contributing to genetic diversity and species transformation:
1. Mutation
Mutations are sudden changes in DNA sequences. They create new genetic variations, which may be beneficial, harmful, or neutral. Mutations are the primary source of raw material for evolution.
2. Natural Selection
Natural selection favors individuals better adapted to their environment. These organisms are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass their traits to the next generation.
3. Genetic Drift
Genetic drift refers to random changes in allele frequencies, especially in small populations. It can lead to the loss of genetic variation over time.
4. Gene Flow
Gene flow occurs when individuals migrate between populations, introducing new genes and increasing genetic diversity.
5. Sexual Selection
Traits that enhance mating success, such as bright colors or elaborate behaviors, are favored even if they do not improve survival.
Evidence Supporting Evolution in Biology
Strong scientific evidence supports evolution in biology, making it one of the most reliable theories in science:
Fossil Record
Fossils provide a chronological record of life, showing gradual changes and transitional forms between species.
Comparative Anatomy
Similar structures in different organisms, known as homologous organs, indicate a common ancestry.
Embryology
Early embryonic stages of different species show similarities, suggesting evolutionary relationships.
Molecular Biology
DNA and protein comparisons reveal genetic similarities between organisms, confirming evolutionary connections.
Types of Evolution
Evolution occurs at different biological levels:
- Microevolution: Small genetic changes within a population
- Macroevolution: Large-scale changes leading to new species
- Convergent Evolution: Unrelated species develop similar traits
- Divergent Evolution: Species evolve different traits from a common ancestor
Speciation and Evolution
Speciation is the process by which new species arise. It occurs when populations become reproductively isolated due to geographical, behavioral, or genetic barriers. Over time, these isolated populations undergo independent evolution in biology, resulting in distinct species.
Importance of Evolution in Modern Biology
Understanding evolution in biology is essential for:
- Developing vaccines and antibiotics
- Improving crop and animal breeding
- Conserving endangered species
- Understanding genetic diseases
- Advancing biotechnology and medicine
Evolution explains why organisms behave the way they do and how life continues to adapt to changing environments.
Common Misconceptions About Evolution
- Evolution does not claim humans evolved from monkeys; both share a common ancestor.
- Evolution is not a theory of chance alone; natural selection is a guided process.
- Evolution is still happening today, not just in the past.
Conclusion
Evolution in biology is a unifying principle that connects all life forms through common ancestry and genetic change. Supported by extensive evidence, it explains the diversity, adaptability, and complexity of life on Earth. For higher-level biology students, understanding evolution is crucial to mastering genetics, ecology, and modern biological sciences.