This article will discuss a variety of topics related to the male reproductive system. We’ll talk about the various components of the male reproductive system, including the seminal vesicles, prostate, urethra, and penis, which are accessory sex organs. We will also look at how they each contribute to the overall reproductive process as well as their individual roles. We will also explore the spermatogenesis procedure, which is the mechanism by which sperm are produced.
What is Reproduction?
The ability of an organism to produce new offspring of its type is called reproduction. Male and female reproductive systems are involved in the process of reproduction.
All living organism maintain their population by reproduction but the way of reproducing is different.
How the way of reproduction is different in different organisms?
In microorganisms, the process of reproduction is called asexual reproduction e.g., budding, fission, etc while in higher animals(which contain completely different reproductive systems) the process of reproduction is complex and is known as sexual reproduction.
Here we will discuss the organs and functions of the human male reproductive system.
Reproduction in humans is sexual i.e., it involves the fusion of both male and female gametes.
~Unique Characters;
The human reproductive system has two unique characteristics;
- The reproductive system does not become functional until it reaches puberty as opposed to other systems which start functional after birth.
- The reproductive systems of males and females are different as opposed to other systems which differ slightly in males and females.
Male Reproductive System:
The reproductive system of males consists of those structures that produce and store Sperm and a few secretions (Seminal fluid, or semen) that help in reproduction.
The male reproductive system is made up of two main parts;
- Primary sex organ
- Accessory Sex Organ
1)Primary sex organ;
Testes are the primary sex organs in males that produce sperm and the male sex hormone (testosterone)
2) Accessory Sex Organ;
Following are the accessory sex organs in males.
i)Seminal vesicles
ii)Prostate gland
iii)Urethra
iv)Penis
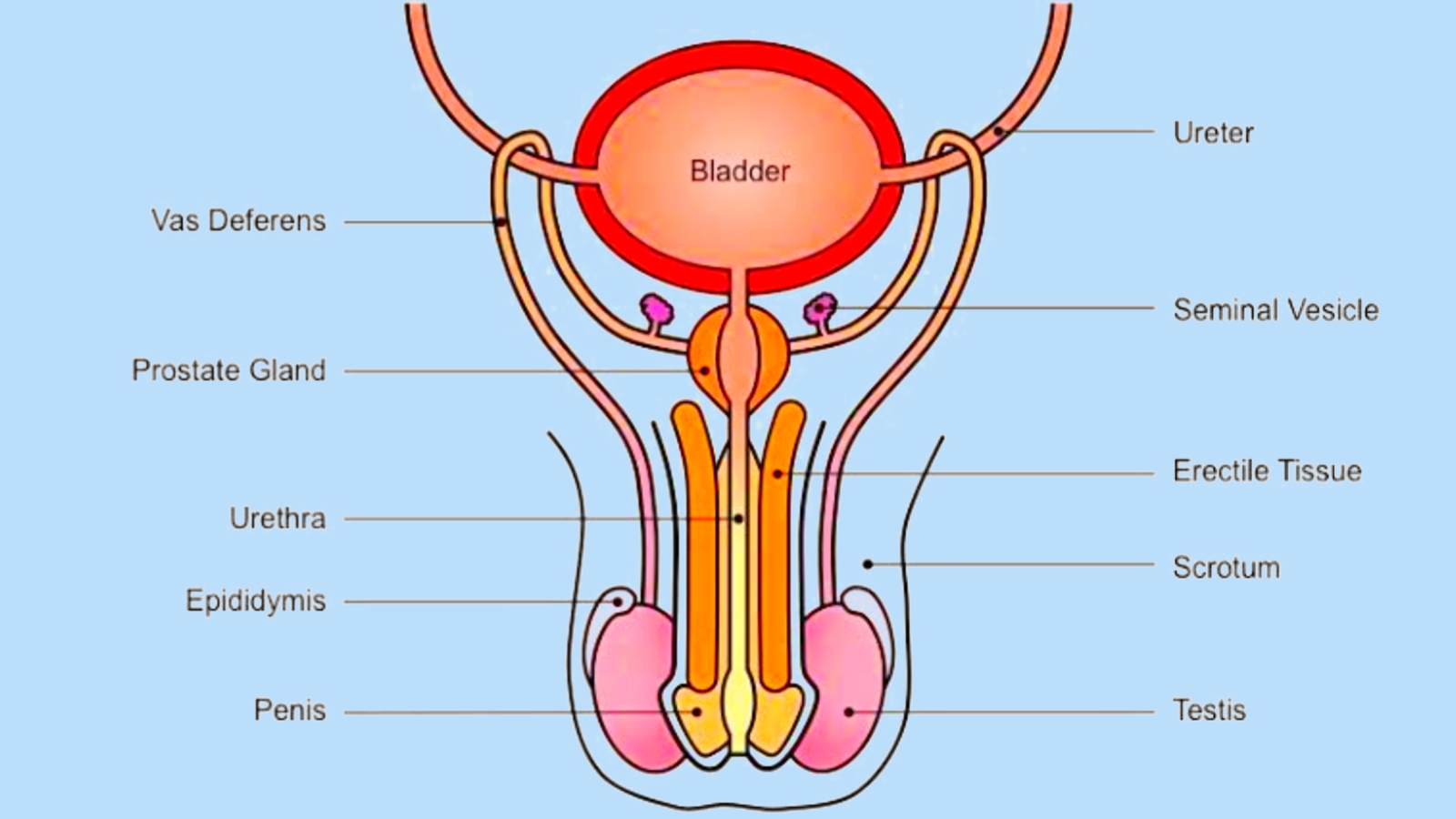
Now we discuss every part of the male reproductive system in detail;
Testes: (singular Testis)
- Testes are the primary sex organ of males.
- Testes are two in number.
- Pair of testes are male gonads.
A) Location;
- Testes(male gonads) are located in a bag of skin called the scrotum which hanged between the thighs.
- The left testis usually lies at a lower level than the right testis.
B) Structure of Testes;
- In human beings males, the testes are oval.
- Each testis weighs about 15 to 19 grams.
- Each testis measures about 5cm in length and 3cm in width.
- Each testis is surrounded by tough three layers from anteriorly and laterally while only one layer posteriorly.
C) Coverings of Testes;
Each testis is covered by three layers;
1)Tunica Vaginalis;
- It is the outermost covering of the testes which is formed by mesothelial cells.
- It consists of two main layers i.e., visceral and parietal layers
- These two-layer glide one another and allow testes for free movement.
- The visceral layer is attached to tunica albuginea and the parietal layer is attached to the inner surface of the scrotum.
2)Tunica Albuginea;
- It is the middle layer of the testes.
- It is formed by dense fibrous capsules.
3)Tunica Vasculosa;
- It is the innermost covering.
- It is made up of connective tissue.
- It contains a huge number of blood vessels.
D) Inner Surface of Testes:
- Tunica Albuginea on the posterior surface thickens which is called mediastinum testes.
- A series of fibrous septa extend from the tunica albuginea which divides the interior of the testes into lobules.
- Within each lobule, there are one to three coiled Seminiferous tubules.
Seminiferous Tubules;
- Seminiferous tubules are thread-like convoluted tubular structures.
- There are about 400 to 600 seminiferous tubules in each testis.
- The length of each seminiferous tubule is about 30 to 70cm.
- The diameter of each seminiferous is about 150 to 300micrometer.
Walls of seminiferous tubules are formed by three layers.
- Tunica Propria(outer layer)
- Thin Homogenous Basement membrane(middle layer)
- Complex Stratified Epithelium(inner layer)
The complex Stratified epithelium is made up of two types of cells.
i)Spermatogenic cells which are also called germ cells
ii)Sertoli cells which are also called Supporting cells.
(Sertoli cells also called sustentacular cells or nurse cells)
*Sperm formation occurs within the Spermatogenic cells while the Sertoli cells help in the formation of sperms.
E) Function of testes:
The two main functions of testes are the following.
1)Spermatogenesis(formation of sperm)
2)Endocrine Function(secretion of some hormones)
1)SPERMATOGENESIS;
*To understand the process of spermatogenesis easily first of all it is mediatory to know the anatomy of the testes.
*The process of spermatogenesis begins at puberty and continues throughout life.
Where spermatogenesis occurs?
The process of spermatogenesis occurs in seminiferous tubules(these tubules are present in testes).
Within seminiferous tubules, there contain two types of cells i.e., germ cells and Sertoli cells.
*Germ cells which are also called spermatogenic cells produce sperm.
*Sertoli cell helps in the formation of sperm.
*Throughout the process of spermatogenesis the spermatogenic cells have cytoplasmic attachment with Sertoli cells.
*Because Sertoli cells provide all the necessary contents for spermatogenesis through cytoplasmic extension.
Definition of spermatogenesis;
The process of formation of male gametes(sperms) is called spermatogenesis.
- The formation of sperm starts from the primitive spermatogenic cells.
- Primitive Spermatogenic cells also called spermatogonia(singular; spermatogonium)
- Each spermatogonium contains a diploid (23 pairs) number of chromosomes.
- Out of 23 pairs of chromosomes 22 pairs of chromosomes are autosomal while the remaining one pair is sex chromosomes.
- The sex chromosomes contain one X chromosome and one Y chromosome.
Spermatogenesis occurs in four stages;
i)Proliferation(Mitotic division of spermatogonia)
ii)Growth(meiotic of type
iii)Maturation
iv)Transformation
i)Proliferation;
*It is the first stage of Spermatogenesis
*The spermatogonia on the inner lining of seminiferous tubules undergo mitosis to form two daughter cells
- Type-A cell
- Type B cell
*In this stage the number of chromosomes in daughter cells does not change.
*Type B cells are pushed towards the lumen where they become primary spermatocytes while Type A cells maintain the germ cell line.
ii)Growth;
*In this stage only the growth of the primary spermatocyte occurs and converts into a large cell.
iii)Maturation;
When the primary spermatocyte reaches full size then it quickly undergoes the meiotic division.
The meiotic division occurs two-phase;
1)First Phase
2)Second phase
First Phase(Meiotic division of Type B cells)
*In this phase the primary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-I to form two secondary spermatocytes.
*Each secondary spermatocyte receives only the haploid(half the number of chromosomes).
Note; Haploid means Half that is 23 chromosomes is the half of 46 chromosomes.
Second Phase(Meiotic division of Secondary Spermatocytes);
*In this phase each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis-II to form two daughter cells called spermatids.
*Each spermatid has a haploid number of chromosomes.
iv)TRANSFORMATION;
*There is no further division. Now the formed spermatids are transformed into mature spermatozoa(functional and motile sperm).
*This transformation phase is called spermiogenesis.
Spermiogenesis is the process by which spermatids are transformed into mature spermatozoa (also called sperm cells).

Accessory Sex Organs in Males
i) Seminal vesicles:
These structures look like pouches and are situated behind the bladder.
The function of Seminal vesicles:
The seminal vesicles secrete a fluid that contains a considerable amount of fructose, prostaglandins, and other components that make up the volume of semen. The sperm receive energy from this fluid, which also supports their movement and survival.
ii) Prostate gland:
The prostate gland is a tiny, walnut-sized gland, which is located underneath the bladder.
The function of the Prostate gland:
The prostate gland creates a milky fluid that makes up a significant portion of semen. The prostate fluid contains Enzymes, citric acid, and zinc found in that aid in nourishing and protecting the sperm. Additionally, it affects sperm activation and aids in sperm motility.
iii) Urethra:
The urethra is a tube that runs through the penis.
The function of the Urethra:
The urethra has both urogenital and reproductive purposes. When a person ejaculates, it transports semen from the ejaculatory ducts to the exterior of the body. Additionally, the urethra carries urine from the urinary tract to out of the body.
iv) Penis:
The penis is the male reproductive system’s exterior organ.
The function of the Penis:
The penis’s primary function during sexual activity is to transport semen to the female reproductive system. This is accomplished by erection, a process in which the penis enlarges and stiffens, enabling penetration and ejaculation.
Additionally, it acts as a passageway for the body’s urine as it leaves the bladder.
The Overall Function of Male Accessory Sexual Organs:
Males’ accessory sex organs are essential to the process of reproduction. Sperm are fed by the seminal vesicles, which also increase their mobility, ensuring their survival and ability to reach the egg. The prostate gland contributes to the volume of semen while also producing fluids that sustain and activate sperm. Both urine and semen can be properly transported due to the urethra’s role as a pathway for both fluids. The penis also aids in ejaculation, which allows sperm to be delivered into the female reproductive system for fertilization. These organs function as a unit to enable males to successfully reproduce.





Greate pieces. Keep posting such kind of info on your
page. Im really impressed by your blog.
Hello there, You’ve performed an incredible job.
I will certainly digg it and in my opinion recommend
to my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this web site.
Thank you for appreciation
Nice blog! Is your theme custom made or did you download it from somewhere?
A theme like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make
my blog jump out. Please let me know where you got your
design. Thanks
I have personally designed the blog
Wow, amazing blog layout! How long have you been blogging for?
you made blogging look easy. The overall look of your site is magnificent,
as well as the content!
I have recently started this blog. Still, the design and contents need an update. Till December it will complete
I don’t know whether it’s just me or if perhaps everybody else experiencing
issues with your website. It seems like
some of the written text in your posts are running off the screen. Can somebody
else please comment and let me know if this is
happening to them as well? This might be a problem with my
internet browser because I’ve had this happen before.
Kudos
Clear the caches of your web browser then the problem will resolve
Thanks very nice blog!
Do you have any video of that? I’d like to find out some additional information.
I would like to thank you for the efforts you have put in penning this blog.
I am hoping to see the same high-grade content by you later on as well.
In truth, your creative writing abilities has motivated me to get my own site now 😉
This is really interesting, You are a very skilled blogger.
I have joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your fantastic post.
Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!
Appreciating the hard work you put into your blog and in depth information you offer.
It’s nice to come across a blog every once in a
while that isn’t the same outdated rehashed material.
Fantastic read! I’ve bookmarked your site and I’m including your RSS
feeds to my Google account.
Thank you so much for appreciation
Hello! Quick question that’s completely off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly?
My site looks weird when browsing from my iphone 4.
I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this problem.
If you have any suggestions, please share. Many thanks!
you have to customize the mobile sections by your own.
Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The
clearness in your post is simply nice and i could assume you are an expert on this subject.
Well with your permission let me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please keep up the rewarding work.
thank you so much for support and such a very nice comment
What a stuff of un-ambiguity and preserveness of precious experience about unpredicted emotions.
I got this site from my friend who informed me concerning this site and now this time I am visiting this website and reading very
informative content at this time.
After I originally commented I seem to have clicked on the -Notify me
when new comments are added- checkbox and from now on whenever a comment is added I get
4 emails with the same comment. There has to be an easy
method you can remove me from that service? Appreciate it!
very nice text very useful