Quiz
Available options: 1 to 25
Pre-Quiz Discussion about Enzymes:
Introduction to Enzymes
Enzymes are biological molecules that act as catalysts to speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They are crucial for various physiological processes, including digestion, metabolism, and DNA replication. These reactions would be too slow to support life without the presence of enzymes.
Composition and Structure of Enzymes
Protein Nature
Enzymes are primarily composed of proteins, which are long chains of amino acids folded into specific three-dimensional shapes. This structure allows enzymes to bind to specific molecules and catalyze reactions efficiently.
Active Site
The active site of an enzyme is a specialized region where the substrate binds. The shape and chemical environment of the active site are complementary to the substrate, facilitating the reaction.
Enzyme Function and Mechanism
Catalysis
Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy of a reaction, which is the energy required to start the reaction. By reducing this energy barrier, enzymes accelerate the rate of the reaction.
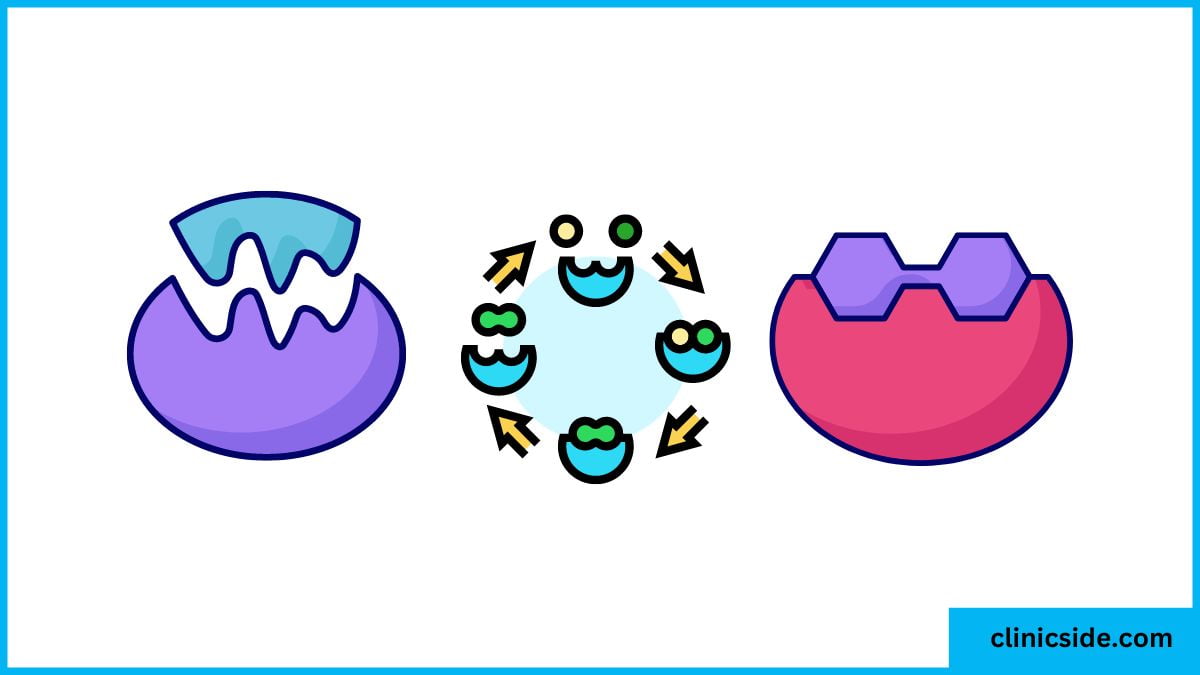
Lock and Key Model
This model describes how enzymes and substrates fit together with high specificity, like a key fitting into a lock. The enzyme’s active site is the “lock,” and the substrate is the “key.”
Induced Fit Model
While the lock and key model emphasizes a perfect fit, the induced fit model suggests that enzyme and substrate undergo conformational changes upon binding to achieve a better fit, enhancing the enzyme’s catalytic activity.
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
Temperature
Enzyme activity is temperature-dependent. Each enzyme has an optimal temperature range within which it functions most efficiently. Excessive temperatures can cause enzymes to lose their shape and functionality, making them inactive.
pH Levels
Enzymes also have an ideal pH range in which they operate most effectively. Deviations from this pH range can alter the enzyme’s structure and impair its functionality. Most human enzymes function best around neutral pH (7).
Substrate Concentration
The rate of enzymatic reactions increases with substrate concentration up to a point. Beyond this saturation point, the rate levels off because all enzyme molecules are occupied.
Enzyme Inhibitors
Competitive Inhibitors
These molecules resemble the enzyme’s substrate and compete for the active site, blocking substrate binding and reducing enzyme activity.
Non-Competitive Inhibitors
These bind to a site other than the active site, inducing a conformational change in the enzyme that reduces its activity. This form of inhibition is independent of the concentration of the substrate.
Types of Enzymes
Amylase
Found in saliva and the pancreas, amylase breaks down starches into sugars, initiating carbohydrate digestion.
Protease
Proteases catalyze the hydrolysis of proteins into smaller peptides or amino acids. They play a vital role in digestion and various cellular processes.
Lipase
Lipases break down fats into fatty acids and glycerol, facilitating fat digestion and absorption.
Catalase
Catalase converts hydrogen peroxide, a harmful byproduct of cellular metabolism, into water and oxygen, protecting cells from oxidative damage.
Enzyme Regulation
Allosteric Regulation
Enzymes can be regulated through allosteric sites, which are sites other than the active site. Binding of molecules to these sites can enhance or inhibit enzyme activity.
Feedback Inhibition
In metabolic pathways, the end product can act as an inhibitor to an enzyme involved in an earlier step. This mechanism prevents the overaccumulation of the product and regulates the pathway efficiently.
Clinical and Industrial Applications
Medical Diagnostics
Enzymes are used in various diagnostic tests. For example, measuring enzyme levels in the blood can help diagnose conditions like liver disease and myocardial infarction.
Therapeutics
Enzyme replacement therapies are used to treat conditions resulting from enzyme deficiencies. For instance, lactase supplements help individuals with lactose intolerance digest lactose.
Industrial Processes
Enzymes are utilized in numerous industrial applications, including food processing, brewing, and biofuel production. They enhance efficiency and reduce the need for harsh chemicals.
Test Guidelines and Time Limit For Quiz:
Guidelines for Maximizing Your Quiz Experience:
Read and Understand:
Carefully read each question related to Enzymes and ensure you have a clear understanding of the concepts before selecting your answer. This will help you make informed choices and avoid misconceptions.
Choose the Best Answer:
Evaluate all available options before selecting the one that aligns best with your knowledge of Enzymes. Strive for accuracy and relevance in your responses.
Time Management:
The quiz has a time limit based on the number of questions you choose. Allocate 45 seconds per question. Manage your time wisely to complete all questions within the allotted time.
Efficient time management increases your likelihood of successfully completing the quiz and submitting your answers within the designated timeframe. Best of luck!





Thanks for sharing
you are truly a just right webmaster The site loading speed is incredible It kind of feels that youre doing any distinctive trick In addition The contents are masterwork you have done a great activity in this matter
Attractive section of content I just stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to assert that I get actually enjoyed account your blog posts Anyway I will be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently fast
I appreciate the logical structure of your arguments,