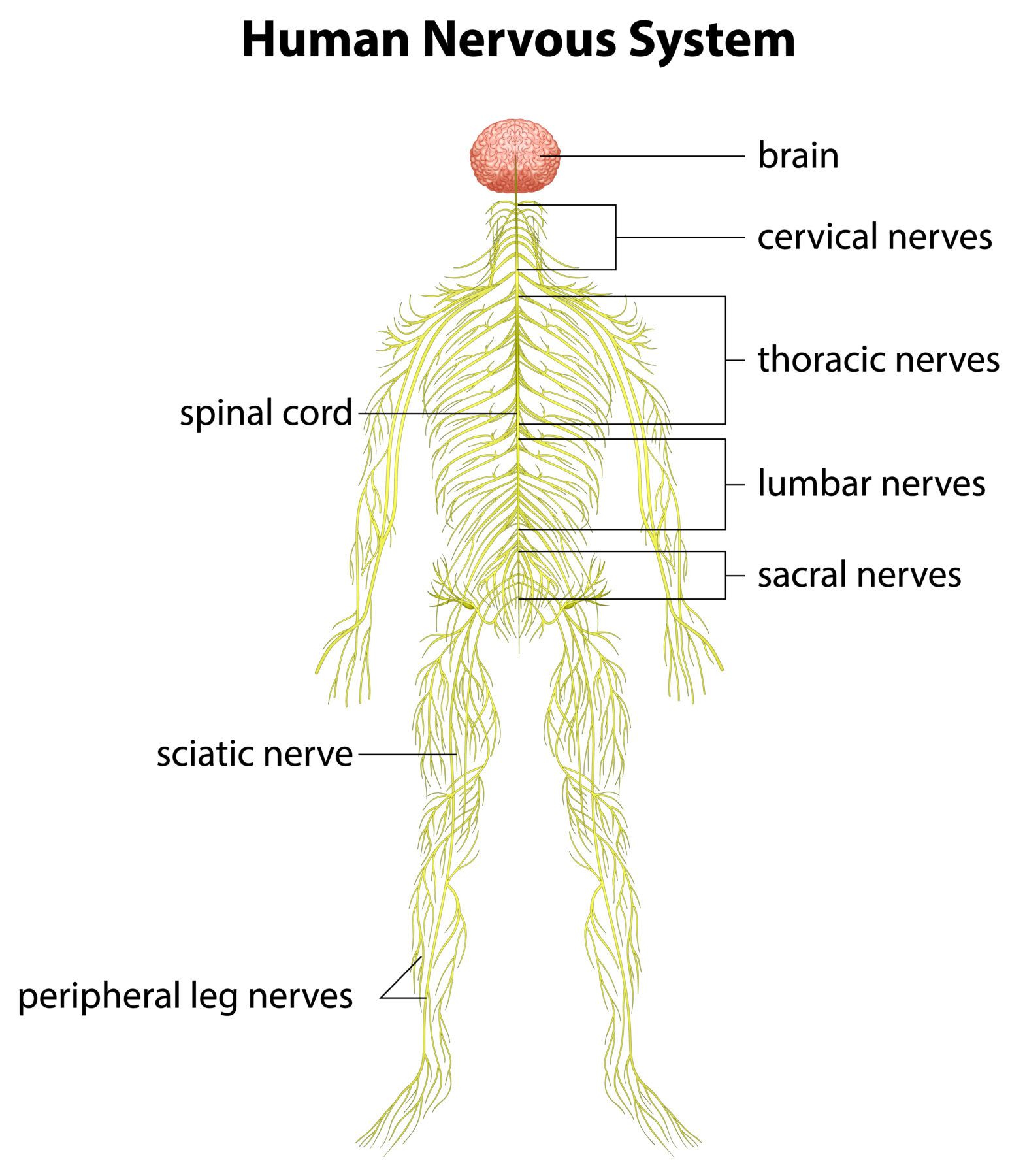
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) is a vital part of the human nervous system that connects the brain and spinal cord to the rest of the body. It acts as a communication bridge, transmitting signals that control movements, sensations, and vital body functions. Without the Peripheral Nervous System, our body would not be able to sense the environment, move muscles, or regulate organs properly.
Quiz
Available options: 1 to 20
What is the Peripheral Nervous System?
The Peripheral Nervous System consists of all the nerves that branch out from the central nervous system (CNS)—which includes the brain and spinal cord—and extend to other parts of the body. These nerves help relay information back and forth, ensuring the body functions in harmony.
The PNS can be divided into two main parts:
- Somatic Nervous System – controls voluntary movements of skeletal muscles.
- Autonomic Nervous System – regulates involuntary actions like heartbeat, digestion, and respiration.
Structure of the Peripheral Nervous System
The Peripheral Nervous System is made up of cranial nerves, spinal nerves, and ganglia:
- Cranial Nerves: There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves that emerge directly from the brain. They control functions such as vision, hearing, taste, smell, and facial movement.
- Spinal Nerves: These 31 pairs of nerves emerge from the spinal cord and extend to different parts of the body. They are responsible for sensory input and motor output.
- Ganglia: Clusters of nerve cell bodies found outside the brain and spinal cord that process and transmit signals between neurons.
Functions of the Peripheral Nervous System
The Peripheral Nervous System has numerous essential functions that keep the body balanced and responsive. Here are some of its major roles:
- Transmission of Sensory Information:
The PNS carries sensory data from the skin, eyes, and other sense organs to the brain for interpretation. - Control of Motor Functions:
It sends motor commands from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, allowing movement. - Regulation of Involuntary Functions:
Through the autonomic nervous system, it manages involuntary activities like heart rate, digestion, and breathing. - Maintaining Homeostasis:
The PNS helps the body adapt to changes in internal and external environments to maintain stability.
Divisions of the Peripheral Nervous System
1. Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
The Somatic Nervous System controls voluntary muscle actions and reflex movements. It includes motor neurons that send messages from the CNS to skeletal muscles, enabling coordination and movement.
2. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The Autonomic Nervous System operates without conscious effort and is further divided into:
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations—known as the “fight or flight” response.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Promotes relaxation and conserves energy—often called the “rest and digest” system.
Both systems work together to ensure body functions like blood pressure, temperature, and respiration remain balanced.
Disorders of the Peripheral Nervous System
Damage or malfunction of the Peripheral Nervous System can lead to several disorders, collectively known as Peripheral Neuropathy. Common causes include diabetes, infections, trauma, and exposure to toxins. Symptoms often include numbness, tingling, pain, and muscle weakness.
Early diagnosis and proper medical care are essential for managing these conditions effectively.
Importance of the Peripheral Nervous System
The Peripheral Nervous System is essential for every action and sensation. From feeling the warmth of the sun to moving your hand away from a hot surface, it ensures smooth coordination between the brain and body.
A healthy Peripheral Nervous System is crucial for:
- Efficient muscle movement
- Accurate sensory responses
- Proper organ functioning
- Maintaining body equilibrium
How to Keep the Peripheral Nervous System Healthy
To support the Peripheral Nervous System, it’s important to adopt healthy lifestyle habits such as:
- Maintaining balanced nutrition with vitamins B1, B6, B12, and E
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
- Managing blood sugar levels
- Regular physical activity
- Getting enough sleep and stress relief
These steps help protect nerves from damage and promote optimal nervous system health.
Conclusion
The Peripheral Nervous System plays a critical role in connecting the brain with the rest of the body. It ensures that our movements, sensations, and vital functions operate smoothly and efficiently. Understanding how this system works deepens our appreciation of the body’s complexity and helps us take better care of our neurological health.