The human body is an amazing machine controlled by an even more complex system — the nervous system. At the heart of this system lies a special kind of cell known as the neuron. Understanding neuron, its structure and types is essential for students of biology and anyone curious about how our brain communicates with the rest of the body.
Quiz
Available options: 1 to 20
What is a Neuron?
A neuron is the basic functional and structural unit of the nervous system. It is a specialized cell responsible for transmitting information throughout the body in the form of electrical and chemical signals.
In simple words, when you touch something hot, it’s the neuron that carries the message to your brain and back to your muscles, helping you react quickly.
The study of neuron, its structure and types helps us understand how thoughts, movements, and sensations happen within milliseconds.
Structure of a Neuron
When studying neuron, its structure and types, it’s important to look at the three main parts that make up a typical neuron:
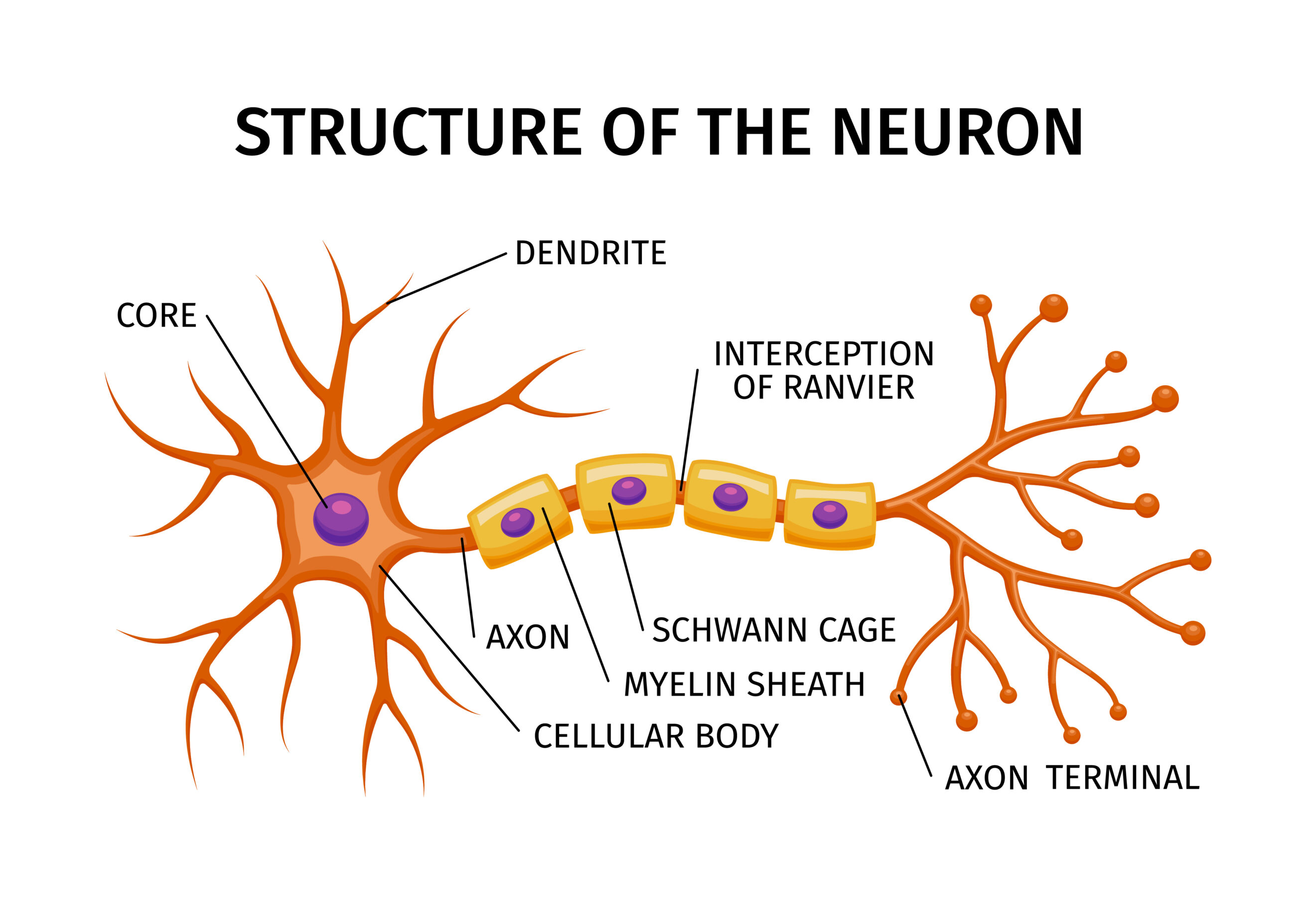
1. Cell Body (Soma)
The cell body or soma contains the nucleus and most of the cell’s organelles. It is responsible for maintaining the cell’s metabolism and health. The nucleus inside the soma controls all neuron activities and contains the genetic material (DNA).
2. Dendrites
Dendrites are short, branch-like extensions that receive incoming signals from other neurons and carry them toward the cell body. They act as the “receivers” in the neuron’s communication system.
3. Axon
The axon is a long, slender projection that transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body toward other neurons, muscles, or glands. The axon is often covered by a myelin sheath, a fatty layer that speeds up the transmission of electrical signals.
Together, these parts form the foundation of neuron, its structure and types, making it possible for signals to travel rapidly through the nervous system.
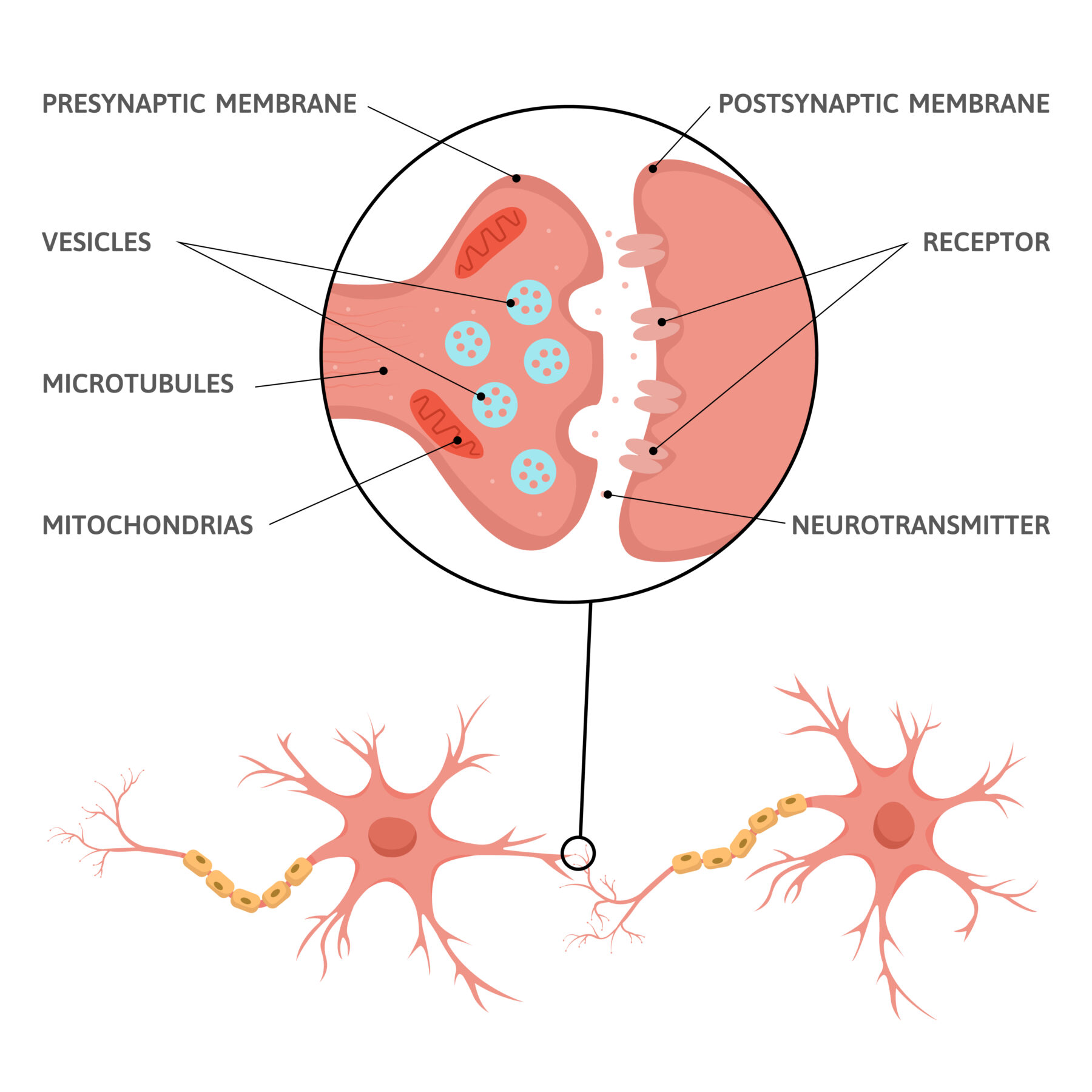
Supporting Structures
In the context of neuron, its structure and types, it’s worth mentioning the axon terminals and synapse:
- Axon terminals: The endpoints of the axon that release neurotransmitters to send messages to the next neuron.
- Synapse: The small gap between two neurons where neurotransmitters carry signals across.
These structures ensure smooth communication between billions of neurons in the body.
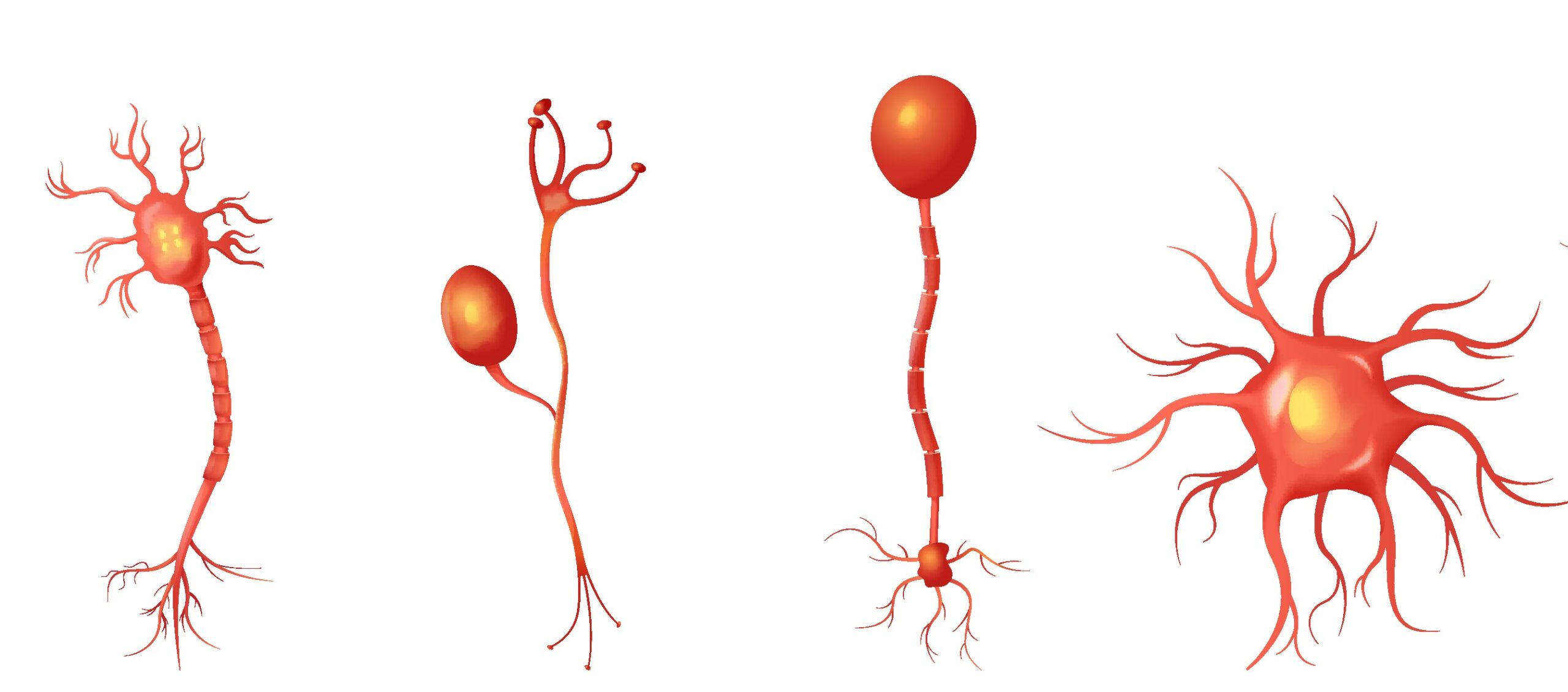
Types of Neurons
There are three major types of neurons, each with a unique function. Understanding these is key to mastering neuron, its structure and types.
1. Sensory Neurons
Sensory neurons carry information from sensory organs (like skin, eyes, ears, and nose) to the brain and spinal cord. For example, when you smell a flower, sensory neurons send that information to your brain.
2. Motor Neurons
Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. They help in performing voluntary actions like walking, writing, or speaking.
3. Interneurons
Interneurons act as a link between sensory and motor neurons. They are found in the brain and spinal cord and help process and interpret information before triggering a response.
These three types — sensory, motor, and interneurons — together explain neuron, its structure and types and how they coordinate to control the human body.
Functions of Neurons
The function of neurons revolves around signal transmission. Some of the main functions include:
- Receiving signals from sensory organs.
- Transmitting information across long distances in the body.
- Processing and responding to stimuli.
- Coordinating voluntary and involuntary actions.
These functions highlight the importance of studying neuron, its structure and types in understanding human physiology.
Importance of Neurons
Without neurons, no communication could occur inside our bodies. Every thought, feeling, and action depends on the efficient working of neurons. Diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are directly linked to neuron damage, making the study of neuron, its structure and types even more vital.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the study of neuron, its structure and types gives us a deeper understanding of how the brain and body communicate. Neurons are the foundation of the nervous system, transmitting signals that control every movement, sensation, and thought. Whether you are a biology student or just curious about how your brain works, exploring neuron, its structure and types is a fascinating journey into the science of life.