Just like animals, plants also need energy to grow, repair, and function. But how do they get that energy without lungs or a circulatory system? The answer lies in the respiratory system in plants. In this blog post, we’ll explore how plants “breathe,” the structures involved, the process of respiration in plants, and how it differs from photosynthesis.
Quiz
Available options: 1 to 20
What is the Respiratory System in Plants?
The respiratory system in plants refers to the process by which plants break down food (glucose) to release energy. This process is called cellular respiration. It occurs in every living cell of the plant and is essential for survival.
Plants absorb oxygen from the environment and use it to break down sugar molecules. This releases energy, which the plant uses to perform essential functions like growth, repair, and transport of nutrients.
The Chemical Equation of Plant Respiration
The general equation for aerobic respiration in plants is:
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide + Water + Energy (ATP)
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Energy
This reaction occurs in the mitochondria of plant cells.
How Do Plants Respire?
Unlike animals, plants do not have specialized respiratory organs. Instead, respiration occurs through the entire surface of the plant, especially in the following structures:
1. Stomata
Tiny pores on the surface of leaves that allow gas exchange (oxygen in, carbon dioxide out).
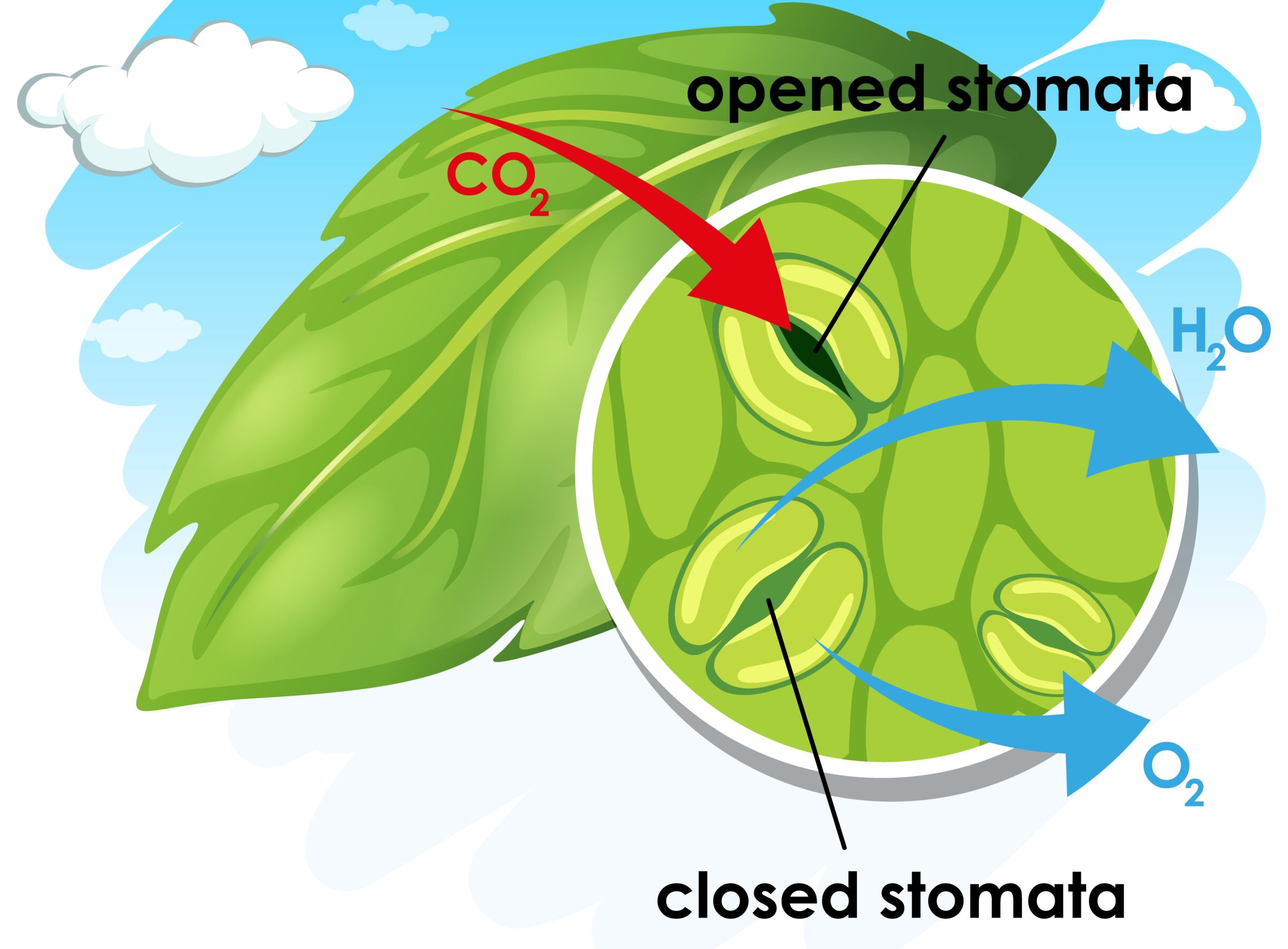
2. Lenticels
Small openings in the stems of woody plants that allow gaseous exchange.
3. Root Hairs
Fine extensions of roots absorb oxygen from air present in the soil.
Types of Respiration in Plants
There are two main types of respiration in the respiratory system in plants:
Aerobic Respiration
- Occurs in the presence of oxygen.
- Most common and efficient.
- Produces a high amount of energy.
Anaerobic Respiration
- Occurs when oxygen is absent (e.g., waterlogged soil).
- Produces less energy.
- Produces alcohol or lactic acid as byproducts.
Differences Between Photosynthesis and Respiration
| Feature | Photosynthesis | Respiration |
|---|---|---|
| Occurs in | Chloroplasts | Mitochondria |
| Uses | Carbon dioxide and water | Glucose and oxygen |
| Produces | Glucose and oxygen | Carbon dioxide and water |
| Requires light? | Yes | No |
| Type of reaction | Energy-storing | Energy-releasing |
Both photosynthesis and the respiratory system in plants are interconnected processes that maintain balance and survival.
Importance of the Respiratory System in Plants
- Supplies energy for metabolic activities
- Helps in active transport of minerals
- Supports growth and cell repair
- Enables root absorption and nutrient movement
Final Thoughts
The respiratory system in plants is a vital process that allows plants to release energy from food. Although they don’t have lungs or blood, plants use stomata, lenticels, and root hairs to carry out gas exchange. Understanding this system helps students see how all living organisms share similar processes for survival.